Products
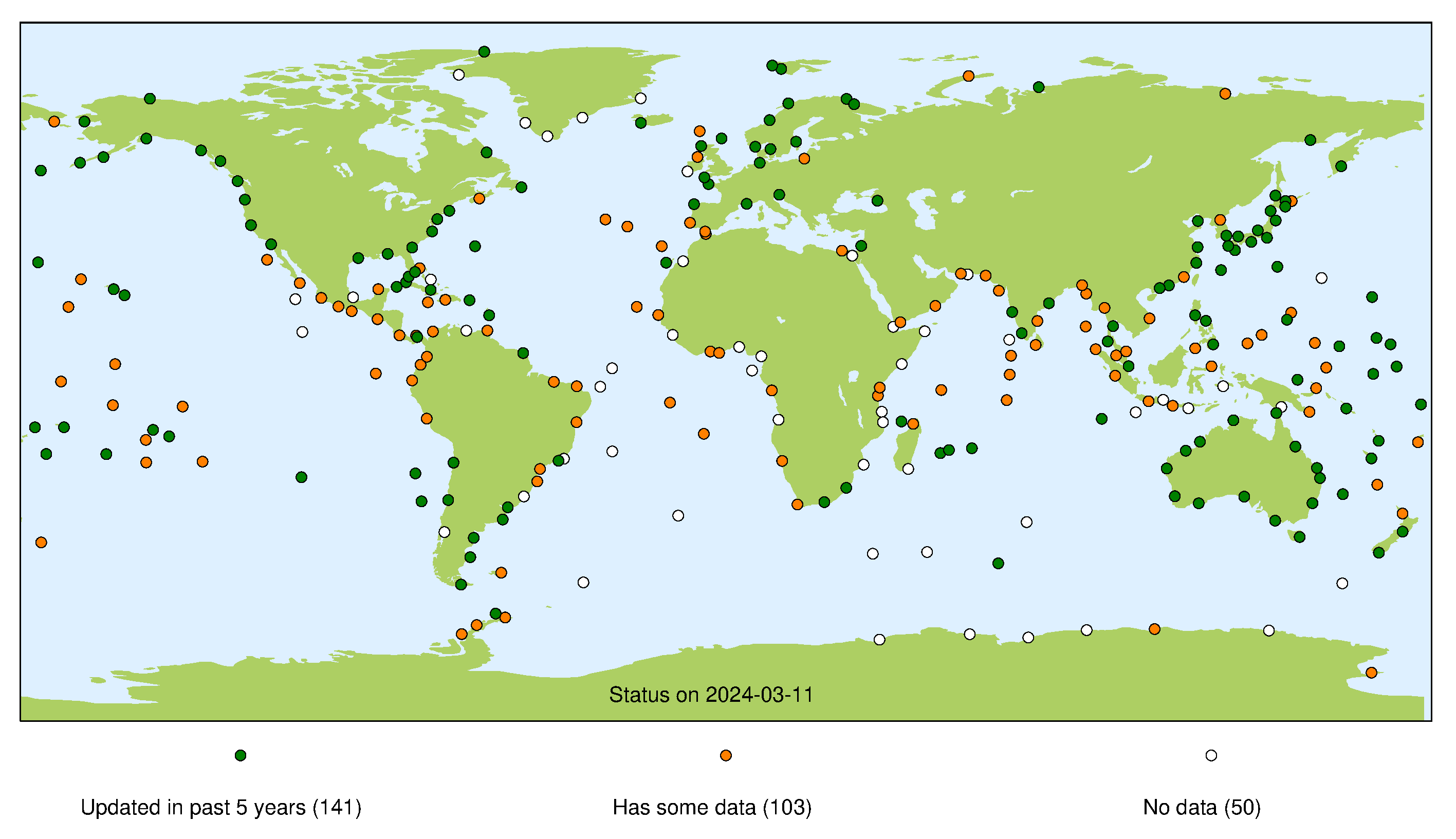
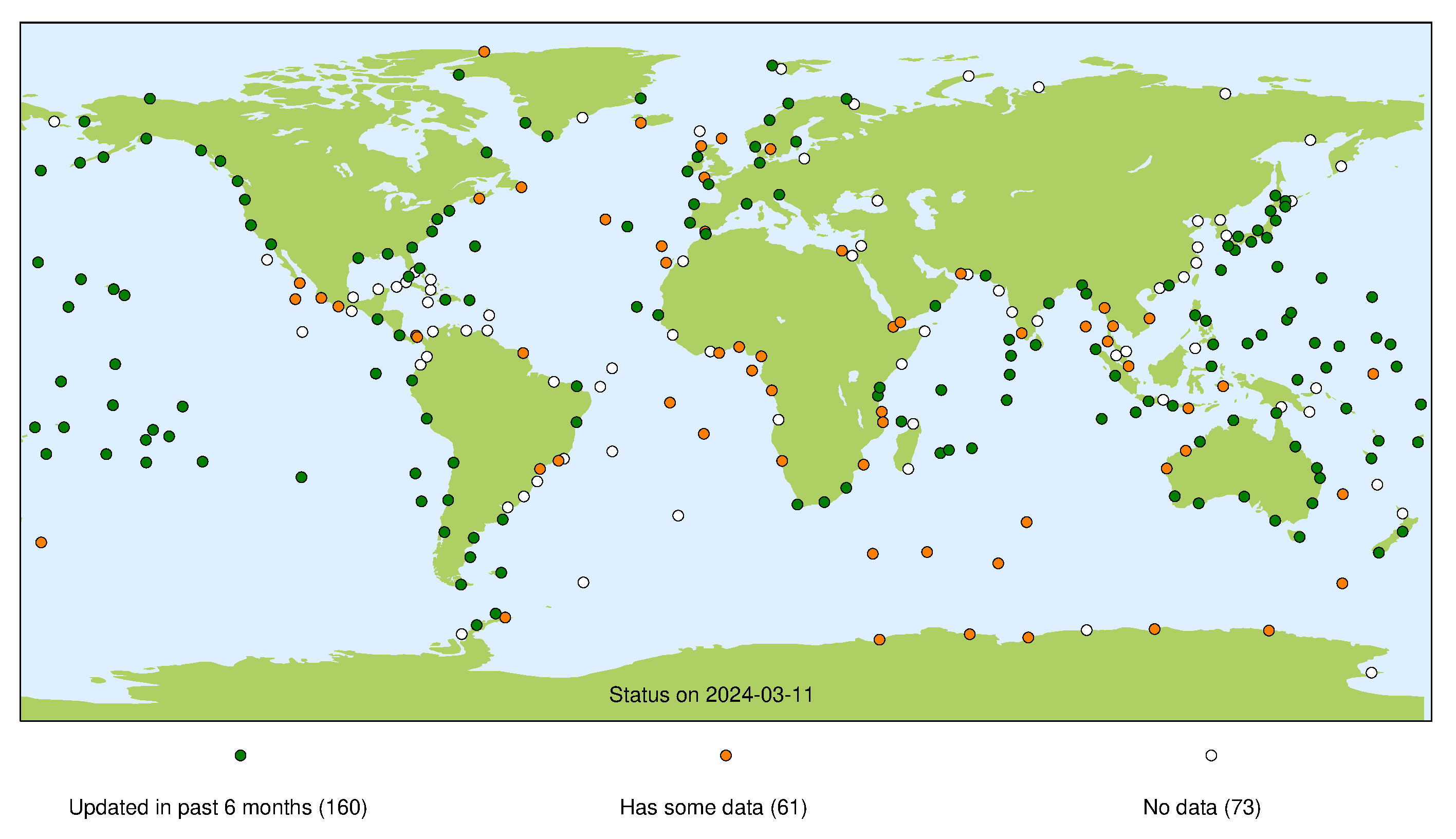
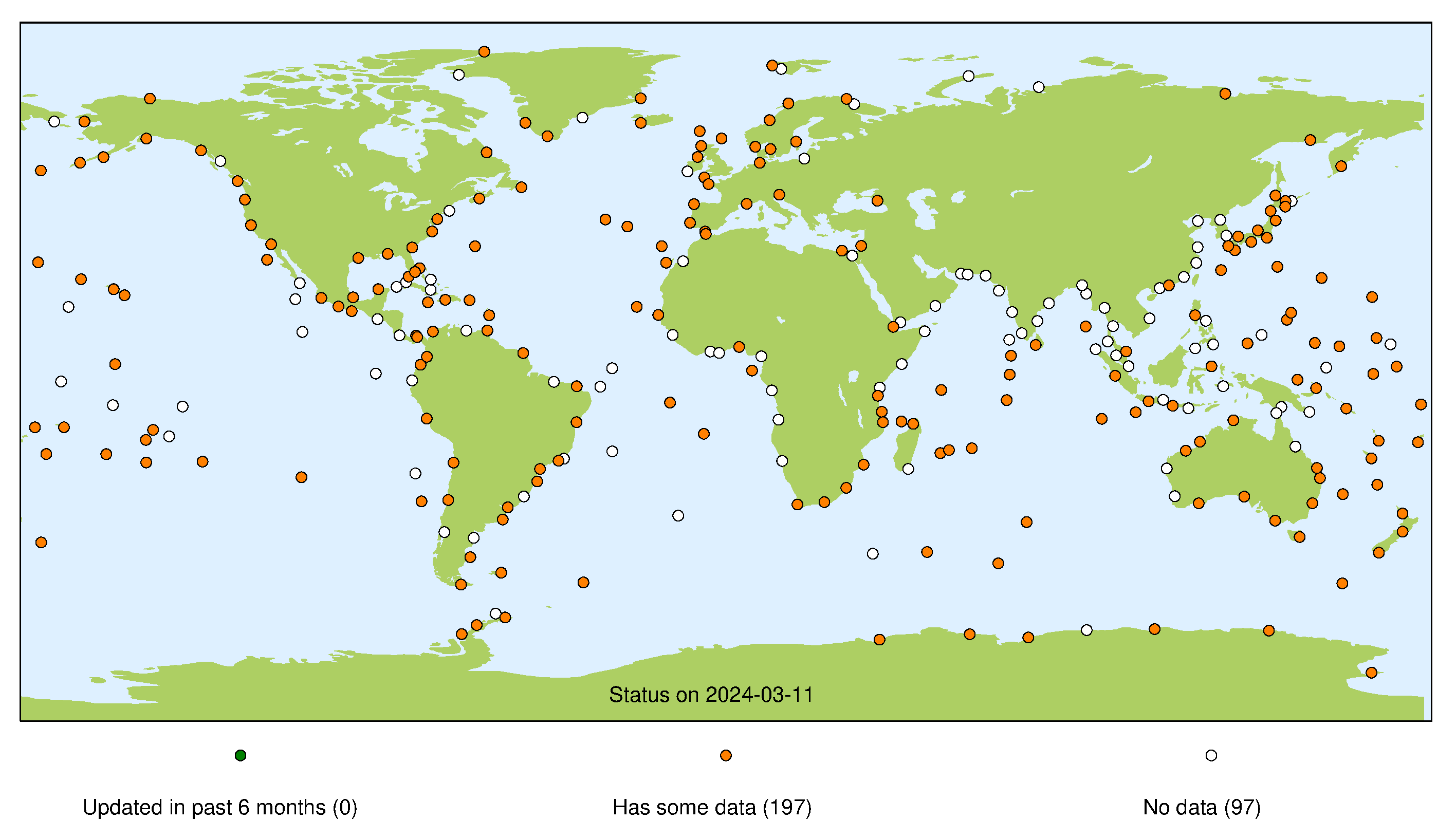
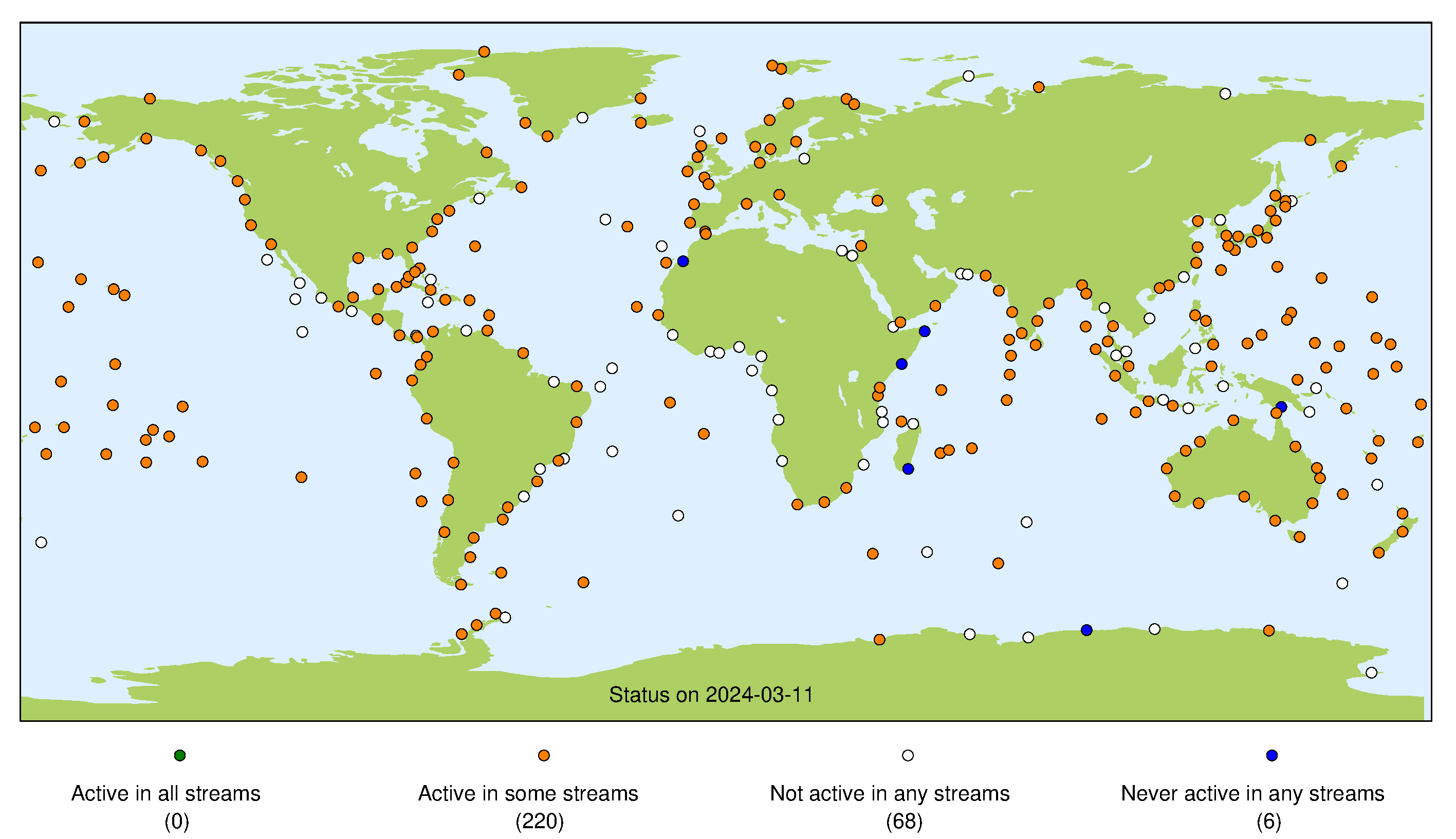
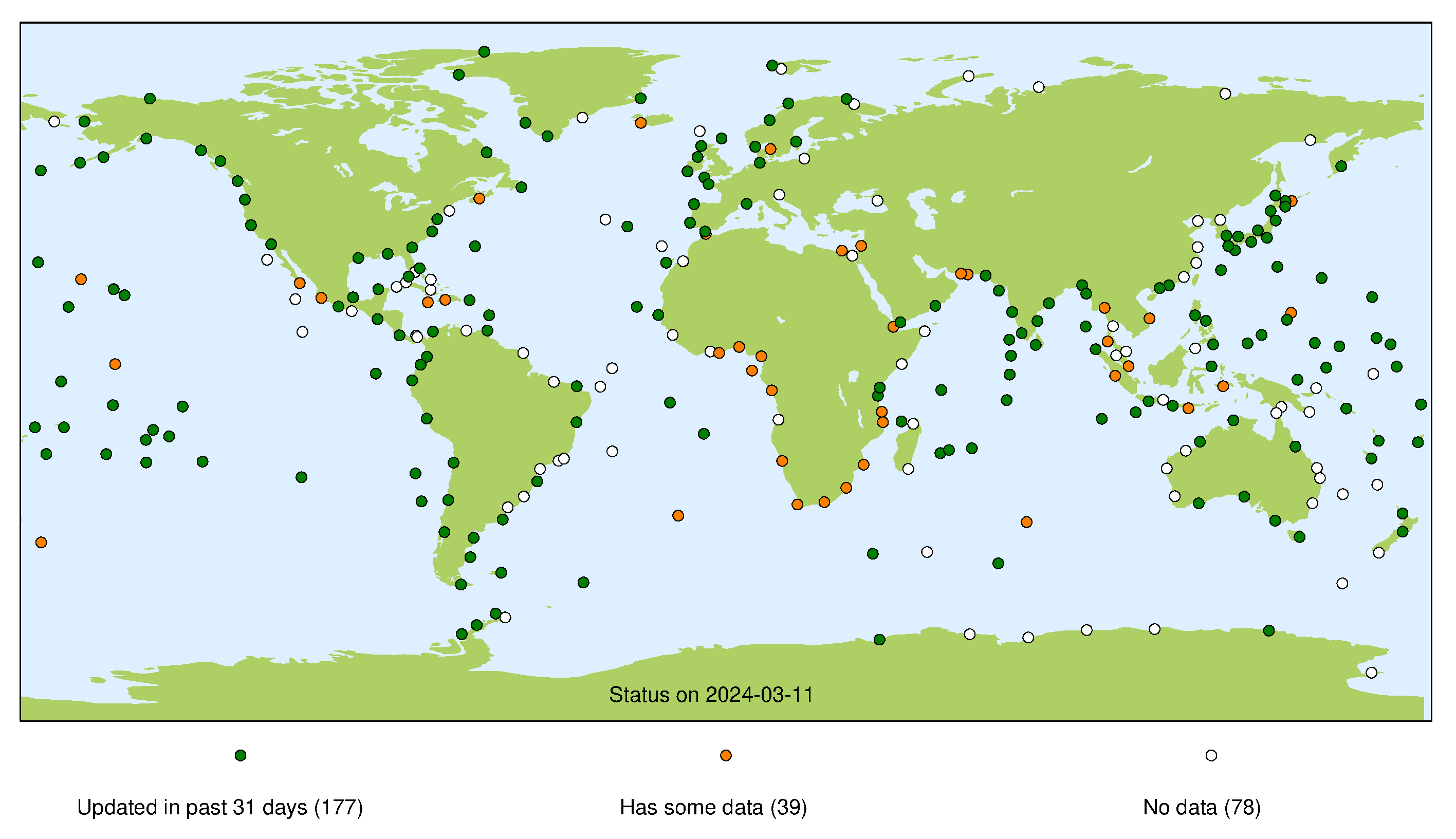
GLOSS Core Network Status
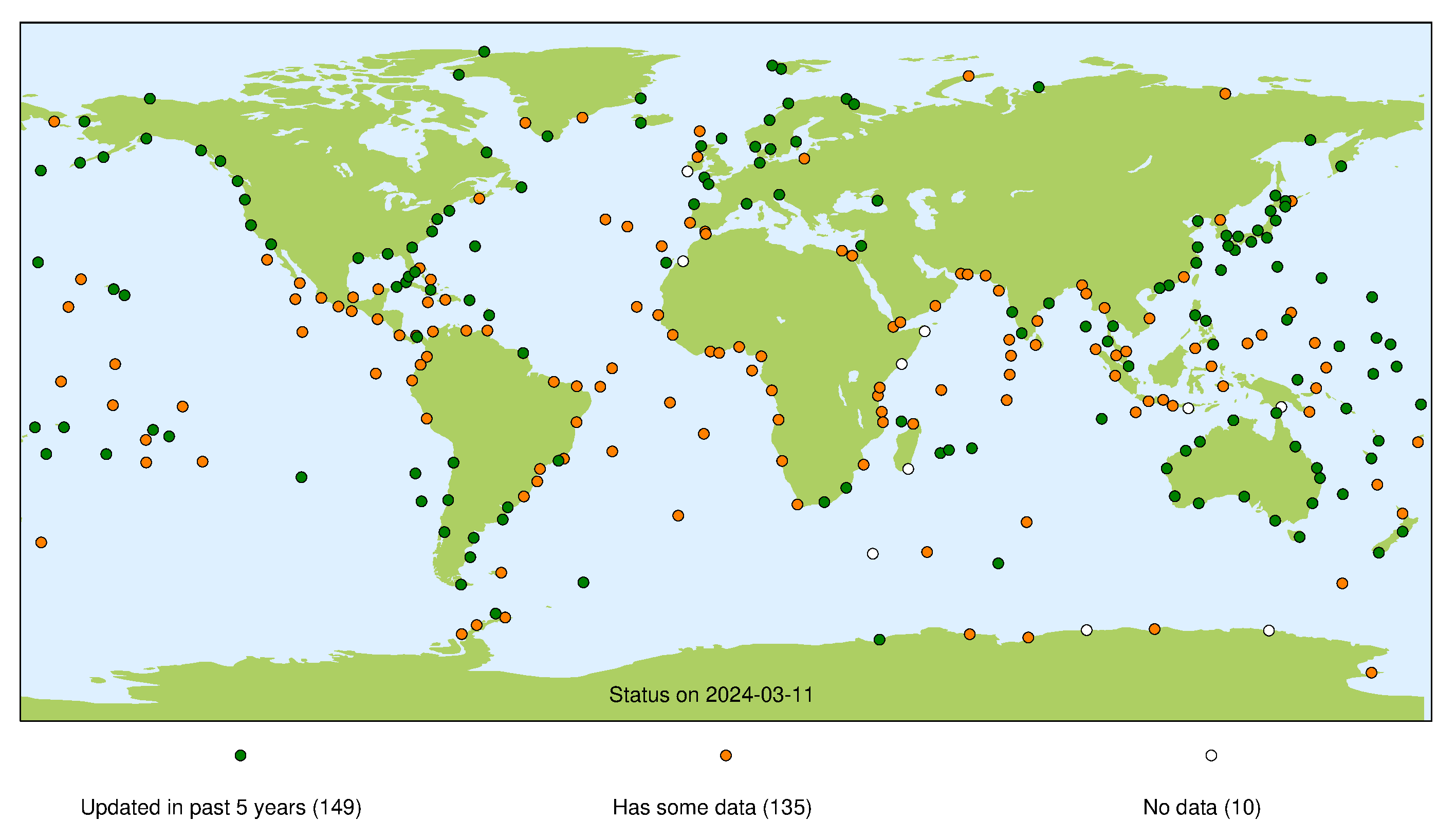
GLOSS Real Time Sea Level Monitoring Network Status at VLIZ
Download image:
png
pdf
eps
Download history
Summary of data streams
- Mean Sea Level Network – mean monthly averages archived by PSMSL. Only the datum controlled portion of the dataset can be used for analysis of long term changes in sea level.
- GLOSS delayed mode – final high frequency averages (hourly) research quality controlled data archived at the British Oceanographic Data Centre (BODC).
- Joint Archive for Sea Level (JASL) – hourly averaged, quality controlled, delayed mode data product archived at the University of Hawaii Sea Level Center (UHSLC) with support of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Ocean Data Center (NODC).
- GLOSS Fast Delivery Network – high frequency delivered within 4-6 weeks after collection, non-quality controlled data, archived at UHSLC.
- GLOSS Real Time Sea Level Monitoring Network – collected at the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ).
- GLOSS GNSS at Tide Gauge Network – data is archived at the SONEL data centre at University of La Rochelle.
Background
The Global Sea-Level Observing System (GLOSS) was established by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) in 1985 to provide coordination for global and regional sea-level networks in support of, and with direction from, the oceanographic and climate research communities. Various tide gauges networks have contributed to GLOSS, each with a different focus and each changing over time as research and operational priorities evolve.
The main component is the GLOSS Core Network (GCN) a global set of 290 tide gauge stations that serves as the backbone of the global in situ sea-level network. The network is designed to provide an approximately even distributed sampling of global coastal sea level variation. Ideally, each station should provide data on a variety of timescales for use in different applications: for example, real time data can be useful for tsunami monitoring, whereas monthly and annual mean data can be used to monitor long terms changes in sea level. In addition, sites should also be fitted with GNSS equipment to monitor land movement at or near the site. For more information on GLOSS please see the GLOSS Implementation Plan 2012.
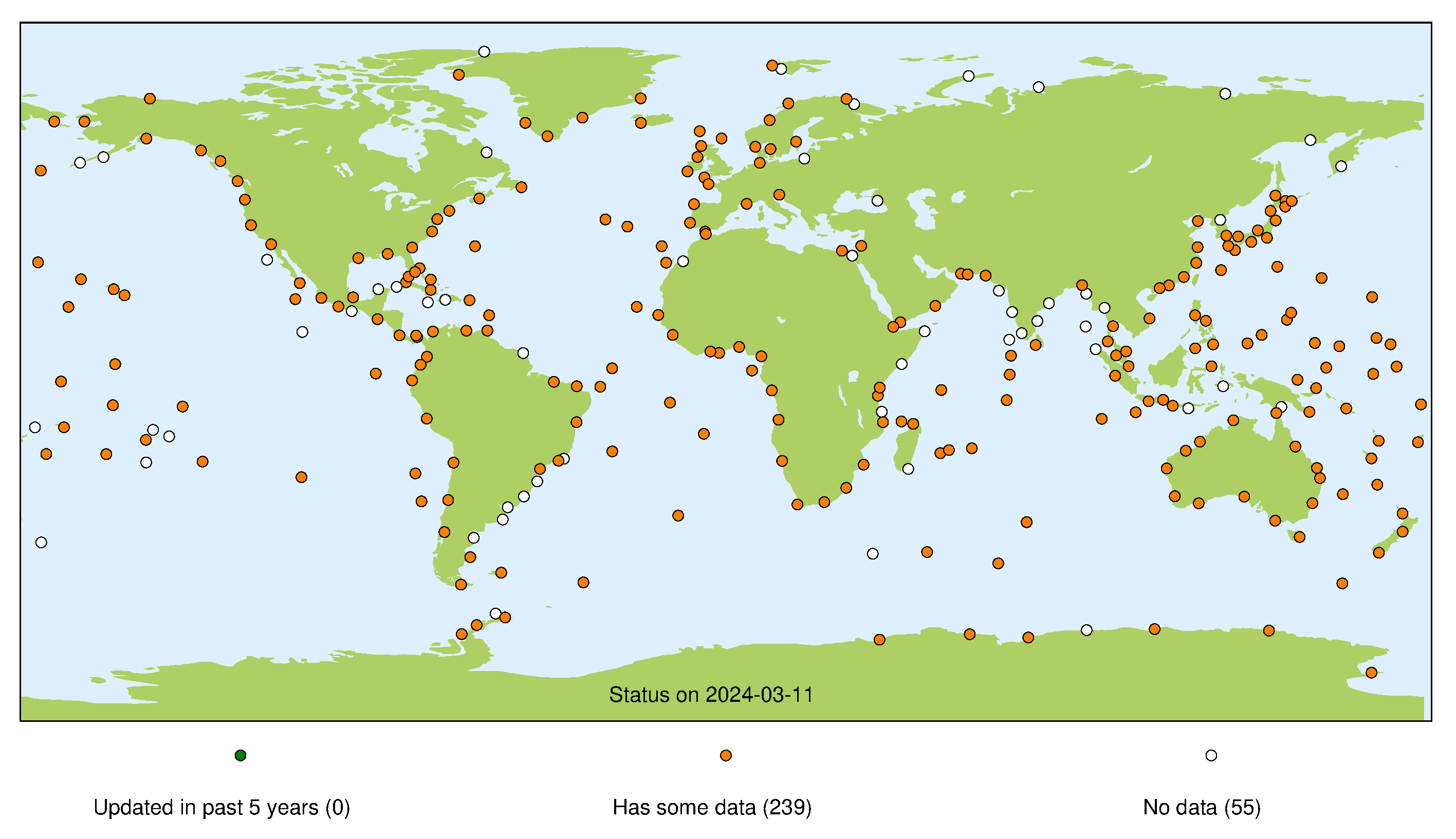
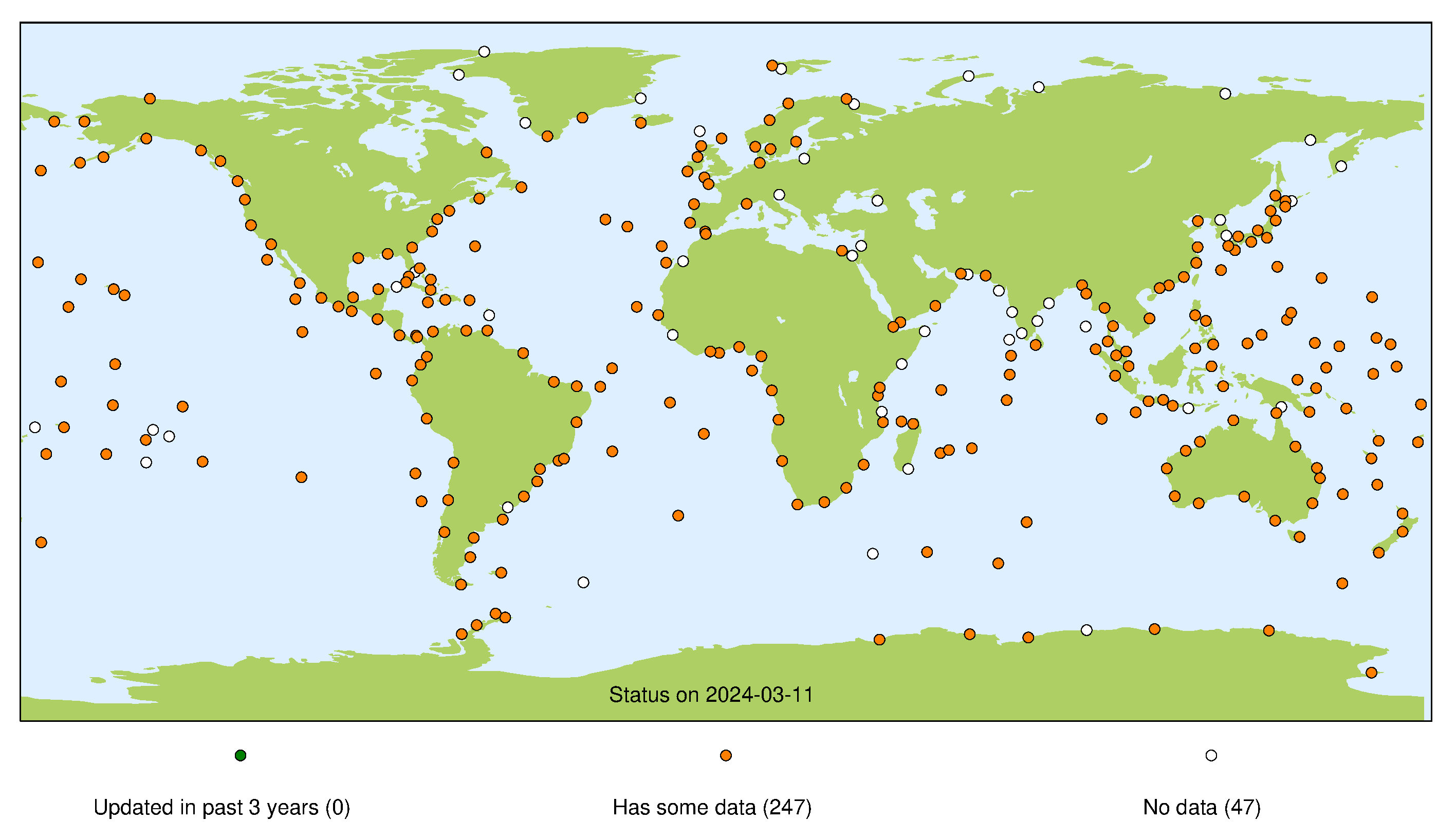
This page presents a summary of the status of the GLOSS Core Network at each of its data centres. For each stream the presented map indicates whether we consider a site operational (green marker), whether a site has been operational in the past (orange marker), or if the site has never operated successfully for that particular stream (white marker). For more information about each individual stream, please refer to our guide to other data sources.
All full summary of network status is available here: glossCoreNetwork.xml